NMN is a kind of anti-aging supplement that has attracted much attention in recent years, and various brands of oral health care products have emerged in an endless stream, so what is NMN? How does it work to help us resist aging? And what kind of aging problems does it protect against?
What is NMN?
NMN (β-nicotinamide mononucleotide) is a precursor of NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide).
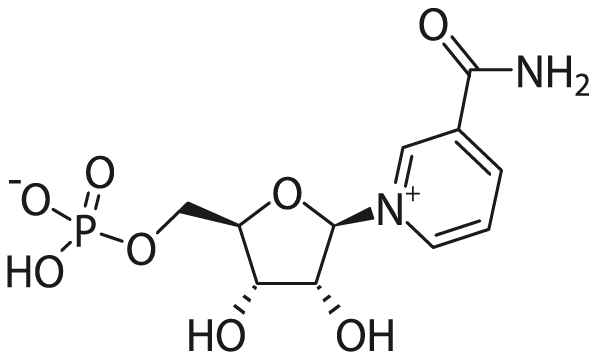
So what is NAD+?
NAD+ is widely distributed in all cells of the human body and is an indispensable coenzyme in the human body.
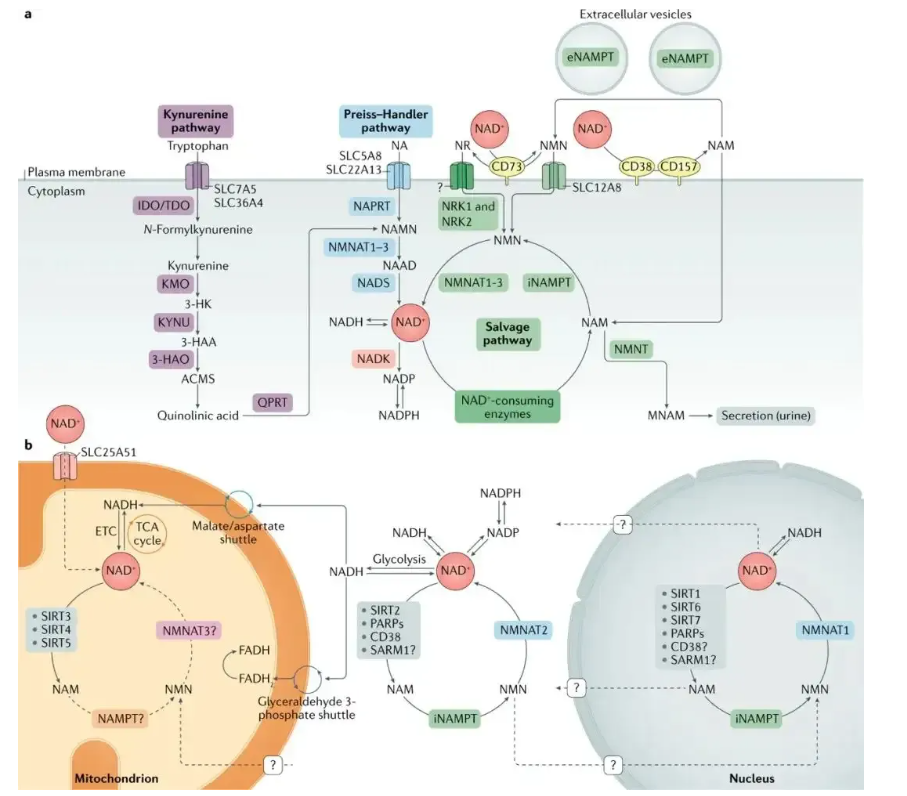
As shown in the figure above, metabolism, REDOX, maintenance and repair of DNA, gene stability, epigenetic regulation, and more all require the involvement of NAD+, which is essential for maintaining overall health and balance.
Therefore, our body has a high demand for NAD+, which is constantly synthesized, broken down and recycled in cells to maintain stable cellular NAD+ levels.
However, during the aging process, the balance of synthesis and decomposition of NAD+ changes, and more is consumed than produced, and the level of NAD+ in the body will naturally decline.
Studies have shown that NAD+ levels drop by as much as 50 percent between the ages of 40 and 60, and low levels of NAD+ are associated with a number of age-related health problems. For example, the body begins to produce muscle degeneration, brain loss, pigment deepening and hair loss, which are collectively referred to as "aging" degenerative symptoms.
How NMN works?
NMN exerts its anti-aging effect by increasing the level of NAD+ in the body.
Studies have shown that supplementing with NMN can effectively increase the content of NAD+, thereby improving the energy metabolism and repair capacity of cells, which is essential for maintaining cell health and function.
At this point, there is a natural question: since NMN is anti-aging by supplementing NAD+, why not directly supplement NAD+ in one step?
Reasons for not directly supplementing NAD+
1. Large molecules and low absorption efficiency
The size of NAD+ molecules is large, and the absorption efficiency in the intestine is low when directly supplemented. NMN molecules are smaller and more easily absorbed into the blood circulation through intestinal epithelial cells.
2. Low intracellular transport level
It is difficult for NAD+ to cross the cell membrane directly into the cell interior.
In contrast, NMN can enter cells more efficiently, where it is quickly converted into NAD+. NMN enters the cell via specific transporters, such as Slc12a8, and is rapidly converted into NAD+ within the cell, thereby increasing the level of NAD+ within the cell.
3. Low stability and high degradation rate
NAD+ is easily degraded and unstable in the digestive tract, while NMN is relatively stable and can be better retained in the body and converted into NAD+.
Ingesting NAD+ directly may be broken down before it enters the bloodstream, reducing its effectiveness.
Therefore, supplementation with NMN rather than directly supplementation with NAD+ was chosen mainly because NMN has higher bioavailability, more efficient cellular uptake, and more stable in vivo transformation.
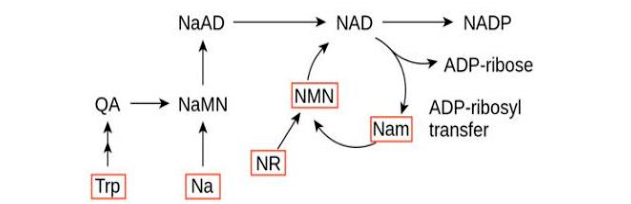
Here is an extension: From the synthesis path diagram of NAD+ above, we can learn that there are 5 precursors. Compared with other complementary methods, why does NMN stand out? It is mainly reflected in the following two aspects:
1. In the way of supplementation, NMN and NR have not been found adverse reactions, and the other three types of products have certain side effects or limited dosage after taking.
2. By comparing NR and NMN, it was found that the improvement effect of NAD+ after NR supplementation was not obvious, while the effect of NMN supplementation was more significant.
Effect of NMN
1. Anti-aging
In 2016, a research team led by Shinichiro Imai, a professor at the University of Washington School of Medicine, conducted long-term experiments with oral NMN in mice. Mice that took NMN orally for 12 months were compared with mice that did not take NMN for normal aging, and it was found that oral NMN was quickly converted into NAD+ in tissues and effectively eliminated various physiological declines related to aging, and NMN did not have any toxicity and side effects.
Supplementation with NMN can also improve mitochondrial function, increase the energy supply of cells, and delay age-related functional decline.
2. Boost metabolism
In 2019, a study by Professor Nina Klimova and others at the University of Maryland School of Medicine found that intrabitoneal injection of NMN significantly increased the level of mitochondrial NAD+ in the hippocampus of laboratory rats, and the level of energy molecule ATP in brain tissue increased, thus improving the body's biological energy metabolism.
In addition, NMN can also increase the activity of antioxidant enzymes in mitochondria and reduce the production of reactive oxygen species.

3. Repair DNA damage
poly ADP ribose polymerase (PARPs) is a DNA repair enzyme that is localized in the nucleus and catalyzes DNA repair under stress, while NMN is an important substrate of PARPs in biological cells.
In 2017, a research team led by Professor David Sinclair at Harvard Medical School discovered how NAD+ repairs DNA damage. As NAD+ levels gradually decline with age, the DNA repair enzyme PARP1 is increasingly bound to DBC1 (Breast cancer deletion factor 1) to form the PARP1 DBC1 complex, which prevents PARP1 from repairing damaged DNA. Increasing NAD+ levels interferes with the formation of the PARP1 DBC1 complex, thereby restoring the DNA repair activity of PARP1.
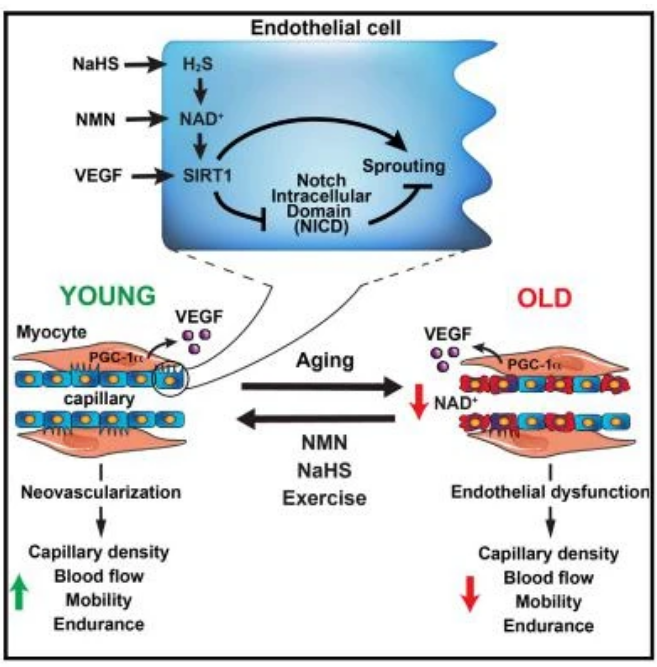
4. Enhance vascular vitality
In 2018, a research team led by Professor David Sinclair at Harvard Medical School found that when 18-month-old mice were given NMN orally for two months, the number and density of capillaries returned to the level of young mice, resting muscle perfusion and dissolved oxygen content also increased, and exercise endurance of the elderly mice increased by 58 to 80 percent. Lactic acid levels in the blood drop after exercise. It can be seen that NMN can improve vascular function, reduce blood pressure and reduce the risk of cardiovascular disease.
5. Control your weight
In 2017, a team led by Professor Margaret J. Morris from the University of New South Wales School of Medicine conducted a series of studies on the role of NMN in weight management and found that in genetically obese mice, both NMN and exercise reduced obesity and improved glucose tolerance and mitochondrial function. However, NMN has a stronger effect on liver fat catabolism (Hadh) and anabolism (Fasn) than exercise, and injection of NNM increases the level of NAD+ in the body and thus activates Sirtuins proteins, increasing the catabolism and anabolism of liver fat.
6. Promote brain health
Risk factors such as diabetes, midlife hypertension, midlife obesity, physical inactivity, and smoking are all associated with vascular dementia and Alzheimer's disease, and maintaining neurovascular function is important for the prevention of neurodegenerative diseases. In 2019, Dr. T arantini S and others from the University of Oklahoma Health Science Center found that intrabitoneal injection of NMN had a significant protective effect on cerebral microvessels of aging mice. NMN alleviated oxidative stress of cerebral microvessels, improved endothelial function and saved neurovascular linkage (NVC) response in the cortex of aging mice. Helps improve cerebral cortex function.
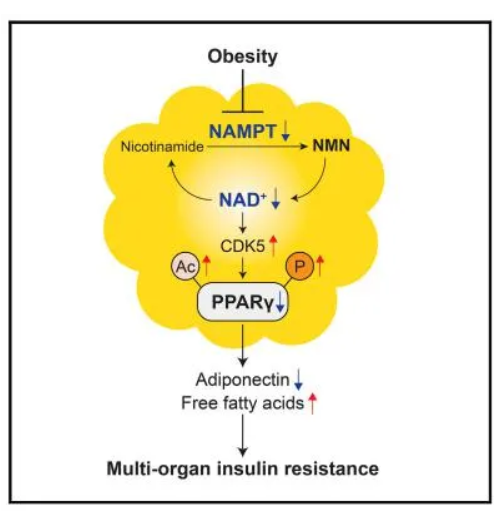
7. Improve insulin resistance to prevent diabetes
Insulin Resistance IR refers to the decreased sensitivity of the target organ to insulin action, that is, the normal dose of insulin produces less than the normal biological effect of a state.
Insulin sensitivity describes the degree of insulin resistance. The lower the insulin sensitivity, the less effective the unit of insulin, the lower the degree of breakdown of sugars. One of the causes of type 2 diabetes is low insulin production; The second is low insulin sensitivity.
A 2016 study by Kelly L. Stromsdorfer, PhD, et al., of the University of Washington School of Medicine, found that decreased levels of NAD+ in the adipose tissue of obese and older mice were associated with severe insulin resistance in multiple organs.
The addition of NMN to the drinking water of mice with insulin resistance caused by the inactivation of specific enzymes can reverse insulin resistance and reduce the concentration of free fatty acids in plasma.
Post time:2024-06-28





